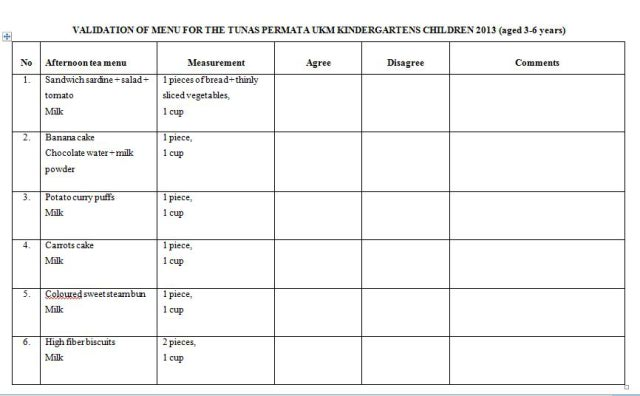
Diet and Warfarin: What You Need to Know
Warfarin is an anticoagulant, or blood thinner, that's used to prevent and treat blood clots and strokes in people with atrial fibrillation, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and other conditions. It's also sometimes used to treat blood clots related to valve replacement surgery or heart attacks. Warfarin is taken orally, and its effectiveness is influenced by many factors, including your diet.
How Diet Affects Warfarin
Vitamin K is a nutrient that's essential for blood clotting. When you take warfarin, it's important to keep your vitamin K intake consistent, as too much or too little can affect its effectiveness.
If you eat foods rich in vitamin K, it can decrease the effectiveness of warfarin and increase your risk of blood clots. If you eat less vitamin K than usual, it can make the warfarin more potent, which can increase the risk of serious bleeding and other side effects, even death.
The amount of vitamin K in foods can vary significantly. For example, a 1-cup serving of raw spinach contains about 143 mcg of vitamin K, while a 1-cup serving of cooked kale contains about 42 mcg.
Foods to Limit
To help keep your vitamin K intake consistent, you should limit your intake of foods that are high in vitamin K. These foods include:
- Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach, kale, collard greens, turnip greens, and mustard greens
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Asparagus
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Green beans
- Peas
- Avocado
- Kiwi fruit
- Prunes
- Grapefruits
- Raisins
- Natto (a Japanese fermented soybean dish)
Foods to Limit or Avoid
In addition to limiting foods that are high in vitamin K, there are also some foods and drinks that can interfere with the absorption of warfarin, which can also lead to changes in its effectiveness. These foods and drinks include:
- Alcohol (especially heavy drinking)
- Grapefruit juice
- Cranberry juice
- Cranberry supplements
- Pomegranate juice
- Pomegranate supplements
- Ginger
- Garlic
Talk to Your Doctor or Pharmacist
Before you start taking warfarin, it's important to talk to your doctor or pharmacist about your diet. They can give you specific recommendations about which foods to limit and avoid. They may also recommend that you take a vitamin K supplement to help keep your intake consistent.
It's also important to let your doctor or pharmacist know about any changes in your diet, such as if you start eating a new food or drink that's high in vitamin K. They can adjust your warfarin dose as needed to keep your intake consistent.
By following these tips, you can help ensure that warfarin is effective and safe for you.
-
Nutritional values of preboiled and parboiled brown rice
QuestionIn your opinion, is preboiled brown rice that takes less
-
A new diet plan
QuestionHello Lela. I would like to eat healthy because Ive rec
-
Increased Metabolism
QuestionHi, Im 18 years old and over the past two years have lost
-
nutrition on a budget
QuestionHello, I will soon be on a tight (students) budget.
-
Coconut oil
QuestionHi, I have been reading that coconut oil is great for coo
-
food pyramid
QuestionHi Leigh-Anne! thanks for ur quick reply! could u please