Liver Cirrhosis: Causes, symptoms and prevention
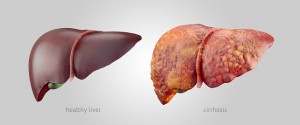 When we discuss liver diseases many of us immediately think of alcohol or drug use. In reality there are actually over 100 different types of liver disease which can impact the function of the liver.
When we discuss liver diseases many of us immediately think of alcohol or drug use. In reality there are actually over 100 different types of liver disease which can impact the function of the liver.
The liver is the only organ in the body with regenerative capabilities. The liver has many different roles, like purifying the blood, detoxing the body, aiding in digestion and storing essential nutrients – just to name a few. Although the liver typically isn’t many people’s concern, it should be because it really is a crucial organ.
Everything we ingest, at some point, passes through the liver, so being mindful of what we take in is important for optimal liver care.
A well-known type of liver disease is cirrhosis. Cirrhosis occurs after fibrosis – scarring done to the liver. It is a response to an already damaged liver, so by the time you receive a diagnosis of cirrhosis, most of the damage has already been done. As scar tissue continues to develop with the worsening of the liver, its ability to perform its many functions deteriorates, making you quite sick.
Causes and symptoms of cirrhosis
 Cirrhosis is a response to scarring on the liver – fibrosis. In an attempt to heal itself the liver produces scar tissue. A build-up of scar tissue leads to a deterioration of liver function.
Cirrhosis is a response to scarring on the liver – fibrosis. In an attempt to heal itself the liver produces scar tissue. A build-up of scar tissue leads to a deterioration of liver function.
There are many different causes of cirrhosis and factors which lead to scarring of the liver, including:
- Hemochromatosis – buildup of iron in the body
- Cystic fibrosis
- Wilson’s disease – copper accumulation
- Biliary atresia – poorly formed bile ducts
- Galactosemia or glycogen storage disease
- Alagille syndrome – genetic digestive disorder
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Hepatitis B and C
- Fat accumulation
- Destruction of bile ducts
- Hardening and scarring of bile ducts
- Infection by parasite
Some of these causes are inherited, other stand alone, and in some people it is a combination of two or more factors.
Symptoms of cirrhosis include:
- Fatigue
- Easy to bleed
- Bruise easily
- Itchy skin
- Jaundice – yellowing of skin or eyes
- Ascites – fluid accumulation in abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Swollen legs
- Weight loss
- Confusion, drowsiness or slurred speech
- Spider-like blood vessels visible on skin
Treatment of cirrhosis
If caught early cirrhosis is treatable. Typically, in order to best treat cirrhosis the cause of the disease must be dealt with. This can refer to treating hepatitis, cessation of alcohol or drug use or treating a parasite.
Complications linked with cirrhosis also need to be treated. This can involve releasing excess fluid from the body, managing blood pressure, treating cirrhosis-related infections and taking medications to reduce toxins in the body.
If cirrhosis is severe a liver transplant is required.
Prevention tips (home remedies) for cirrhosis
 Cirrhosis is not inevitable, and you can begin to start taking steps to protect your liver and prevent cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis is not inevitable, and you can begin to start taking steps to protect your liver and prevent cirrhosis.
Limit or cut out alcohol. Alcohol isn’t just linked with cirrhosis, it can also play an overall role in poor liver function.
Choosing a healthy diet can promote liver function as well. Steer clear of fatty, fried foods and stick with fruits, vegetables and lean meats; red meat takes longer to break down in the liver.
Maintain a healthy weight; some forms of liver disease, including cirrhosis, are linked with fat accumulation.
Reduce your risk of developing hepatitis. Do not share needles, ensure you are vaccinated, and be aware of the risk of hepatitis when traveling to foreign countries.
Avoid infections. Cirrhosis makes it difficult to fight off infections. Avoid people who are sick and wash your hands frequently
Eat a low-sodium diet. High sodium can cause your body to retain fluids, worsening swelling in your abdomen and legs. Use herbs for seasoning your food, rather than salt. Choose prepared foods that are low in sodium.
How to lower elevated liver enzymes
Elevated liver enzymes may indicate a problem with the liver. When elevated liver enzymes occur, the liver may become inflamed and release higher than normal chemicals. The release of these enzymes can be seen in a blood test that your doctor can diagnose. Continue reading…
-
Weight Loss Issues Can You Be Cellulite Free
One thing I really must say at the outset of this article is, that if
-
Menopause and Osteoporosis
We know that our bodies require calcium and vitamin D in order to
-
Weight Loss Tips For The Normal Person
Are you searching to lose fat for you to improve your appearance, your
-
Gastric Sleeve Cost - A Guide To The Cost Of Gastric Sleeve Surgery
When comparing the cost of gastric sleeve surgery, it is important to
-
Personalized Weight Loss Plans Breaking The YoYo Cycle Of Failed Diets
Dieting will continue to fail most dieters, unless personalized weight
-
Burn Your Fat Like I Did – The Female Version
So where do I start? It has been a long and drawn out process for me t
- DON'T MISS
- Remembering The Titanic Top Ten Weight Loss Mistakes Others Make But We Can Avoid
- Benefits of Herbal Weight Loss Patches
- 10 Essencial Tips How To Lose 10 Pounds In 2 Weeks Quickly
- They Lie To You About Your Weight
- Tips To Help Shed The Pounds Off!
- Is surgical procedure as a treatment for obesity truly a Painless Way to Weight reduction?
- Information About the Paleo Diet
- Natural Apple Cider Vinegar Weight Loss Tip
- Probably The Best Weight Loss Program Ever
- Book Review - Ultrametabolism: The Simple Plan for Automatic Weight Loss




